What is Pneumatic Equipment? Understanding Types and Applications Explained
Pneumatic equipment plays a crucial role in modern industrial operations, providing efficient and reliable solutions for a variety of tasks. As John Smith, a renowned expert in the field of pneumatic systems, stated, "Pneumatic equipment is not just about power; it's about precision and control in the dynamic world of manufacturing." With its ability to harness compressed air for automation and manipulation, pneumatic equipment is essential across diverse applications, from assembly lines to material handling.
Understanding the different types of pneumatic equipment and their specific applications is vital for industries seeking to optimize performance and reduce operational costs. This introduction aims to elucidate the fundamental concepts of pneumatic equipment, including its various forms such as actuators, compressors, and valves, while highlighting their significance in enhancing productivity and safety. By delving into the functionality and advantages of these systems, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and objectives, ultimately ensuring a seamless production process.

What is Pneumatic Equipment? A Comprehensive Overview
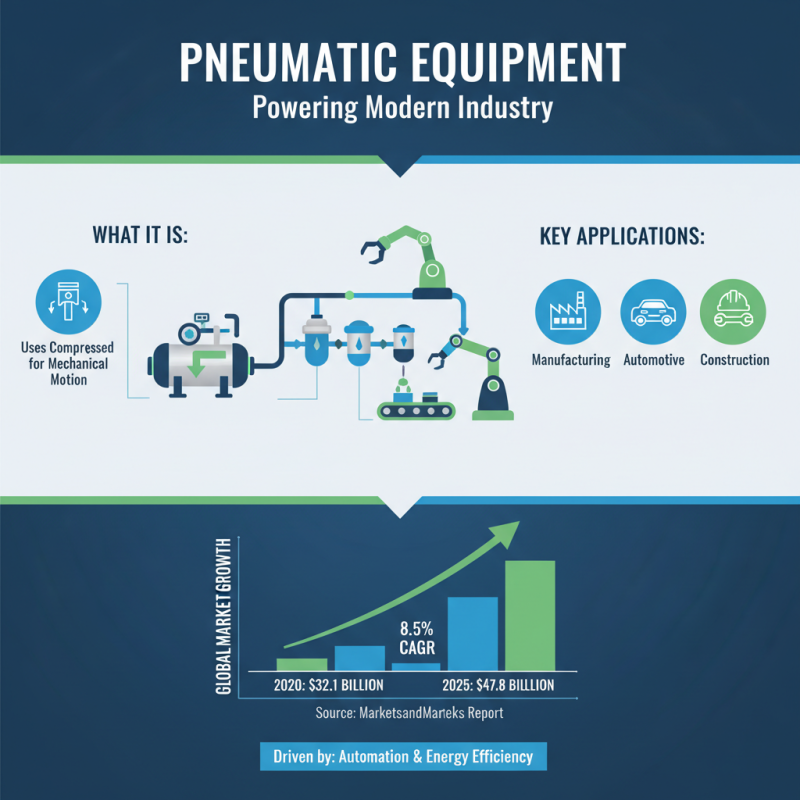
Pneumatic equipment, defined as devices that use compressed air to produce mechanical motion, is integral to various industrial applications. This type of equipment is primarily utilized in sectors such as manufacturing, automotive, and construction, where efficiency and automation are crucial. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global pneumatic equipment market is projected to grow from $32.1 billion in 2020 to $47.8 billion by 2025, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.5%. This growth is attributed to the increasing demand for automation and the rising adoption of energy-efficient technologies.
A comprehensive overview of pneumatic equipment reveals several types, including pneumatic actuators, compressors, valves, and tools. Pneumatic actuators convert compressed air into mechanical energy, facilitating motions like lifting, pushing, and rotating. Tools powered by pneumatic systems, such as air wrenches and sanders, are renowned for their lightweight design and high power-to-weight ratio, enhancing productivity. The versatility of pneumatic systems allows for their application across various processes, from assembly lines to packaging. Additionally, as industries shift towards sustainable practices, pneumatic technologies that reduce energy consumption and improve operational efficiency have gained traction, thus underscoring the significance of pneumatic equipment in modern industrial operations.
Key Components of Pneumatic Systems: Understanding Their Functions
Key components of pneumatic systems play a crucial role in their functionality and overall performance. At the heart of any pneumatic system lies the air compressor, which generates the necessary compressed air. This compressed air is then distributed through a network of pipes and fittings, ensuring the energy is delivered where it is needed. Alongside the compressor, other essential components include pneumatic cylinders, which convert the compressed air into mechanical motion to perform tasks such as lifting, pushing, or driving machinery. These cylinders come in various sizes and formats, allowing for flexibility in applications ranging from automotive assembly to packaging.
Another integral part of pneumatic systems is the control valves, which regulate the flow and pressure of compressed air. These valves ensure that the air is directed appropriately to different components, facilitating smooth operation and precise control. Furthermore, filters and lubricators are essential to maintain the quality of the compressed air, preventing contaminants from causing damage to the system. By understanding the functions of these key components, users can better appreciate how pneumatic systems operate and their widespread applications across various industries, including manufacturing, construction, and material handling.
Types of Pneumatic Equipment: Classification and Uses in Various Industries
Pneumatic equipment plays a crucial role across various industries by utilizing compressed air to perform work, which makes it a flexible and efficient tool for many applications. The primary types of pneumatic equipment include pneumatic cylinders, valves, actuators, and hoses. Pneumatic cylinders convert compressed air into mechanical motion, allowing for precise linear movement, which is vital in manufacturing and automation processes. Valves control the direction and flow of air, ensuring that systems operate smoothly and efficiently. Actuators, which may be rotary or linear, translate pneumatic energy into movement, empowering machines to perform tasks with speed and accuracy.
In terms of applications, pneumatic equipment is widely used in sectors such as automotive, food processing, electronics, and construction. In automotive assembly lines, for instance, pneumatic tools facilitate the rapid fastening of components, which not only increases productivity but also enhances worker safety by reducing manual labor strain. The food processing industry leverages pneumatic systems for packaging and conveying, ensuring hygiene and efficiency. Additionally, in electronics manufacturing, pneumatic equipment aids in the delicate positioning and assembly of components, demonstrating its versatility and integration into modern industrial practices. By understanding these types and their uses, companies can better implement pneumatic solutions that optimize performance and streamline operations.
What is Pneumatic Equipment? Understanding Types and Applications Explained
| Type of Pneumatic Equipment | Description | Applications | Industries |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air Compressor | A device that converts power into potential energy stored in pressurized air. | Powering tools, inflating tires, painting. | Manufacturing, Automotive, Construction |
| Pneumatic Cylinder | A mechanical device that uses compressed air to produce linear motion. | Actuating machinery, material handling. | Packaging, Food Processing, Robotics |
| Pneumatic Actuator | A device that uses compressed air to create rotational or linear motion. | Controlling valves, opening and closing machinery. | Oil & Gas, Water Treatment, HVAC |
| Pneumatic Tool | Tools powered by compressed air for various tasks. | Drilling, grinding, cutting. | Construction, Automotive, Maintenance |
| Pneumatic Conveyor | A system that uses air pressure to move materials. | Transporting bulk materials, powders. | Food Processing, Mining, Pharmaceuticals |
Applications of Pneumatic Equipment: Benefits Across Different Sectors
Pneumatic equipment plays a crucial role in various industries due to its efficiency and versatility. Its applications span across manufacturing, construction, automotive, and even medical sectors.
In manufacturing, pneumatic systems are used for automation processes, enabling tasks such as material handling, assembly, and packaging to be performed with speed and precision. The inherent ability of pneumatic tools to deliver high power-to-weight ratios makes them ideal for tasks that require both agility and strength, reducing the physical strain on workers while enhancing productivity.
In the construction industry, pneumatic equipment is often utilized for demolition, drilling, and driving fasteners. Air-powered tools are favored for their robustness and ability to operate in challenging environments where electricity might not be readily available. Moreover, in the medical field, pneumatic systems are increasingly being integrated into surgical devices and hospital equipment, facilitating procedures that require controlled and delicate operations.
The adaptability of pneumatic technology to meet the diverse needs across sectors underscores its importance in advancing efficiency, safety, and overall operational effectiveness.
Future Trends in Pneumatic Technology: Innovations and Market Projections
The future of pneumatic technology is poised for significant transformation driven by innovations that enhance efficiency and adaptability across various industries. According to a recent report by Market Research Future, the pneumatic equipment market is projected to reach a valuation of over $23 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of approximately 6.5% from 2020 to 2027. This growth is primarily attributed to advancements in automation and robotics, which increasingly rely on pneumatic systems for their ability to provide precise control and operational flexibility.
Innovations such as smart pneumatic systems, which integrate IoT technology, are leading the way in enhancing operational efficiency and real-time data monitoring. The latest industry analysis indicates that these smart systems can reduce maintenance costs by up to 30% while improving energy efficiency. Furthermore, emerging applications in sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, and construction highlight the versatile nature of pneumatic solutions.
Companies are investing in these technologies not only to streamline operations but also to align with sustainability goals, as pneumatic systems often consume less energy compared to traditional mechanical systems. With market projections indicating a robust demand for pneumatic solutions, industries are gearing up to adopt these innovations as they prepare for a more automated and efficient future.
Related Posts
-

Revolutionizing Water Management with the Latest Mini Submerged Pump Innovations
-

Mastering the Jack Hammer Manual: Essential Tips and Techniques for Efficient Use
-

Exploring the Industry Trends of Jack Hammer Manual at the 2025 China Import and Export Fair
-

Top 10 Best Vertical Slurry Pumps for Efficient Slurry Management
-

Exploring the Benefits of Portable Ventilators: Your Guide to Respiratory Relief Anytime, Anywhere
-

Why Invest in Mining LED Headlamps for Enhanced Safety and Efficiency?



